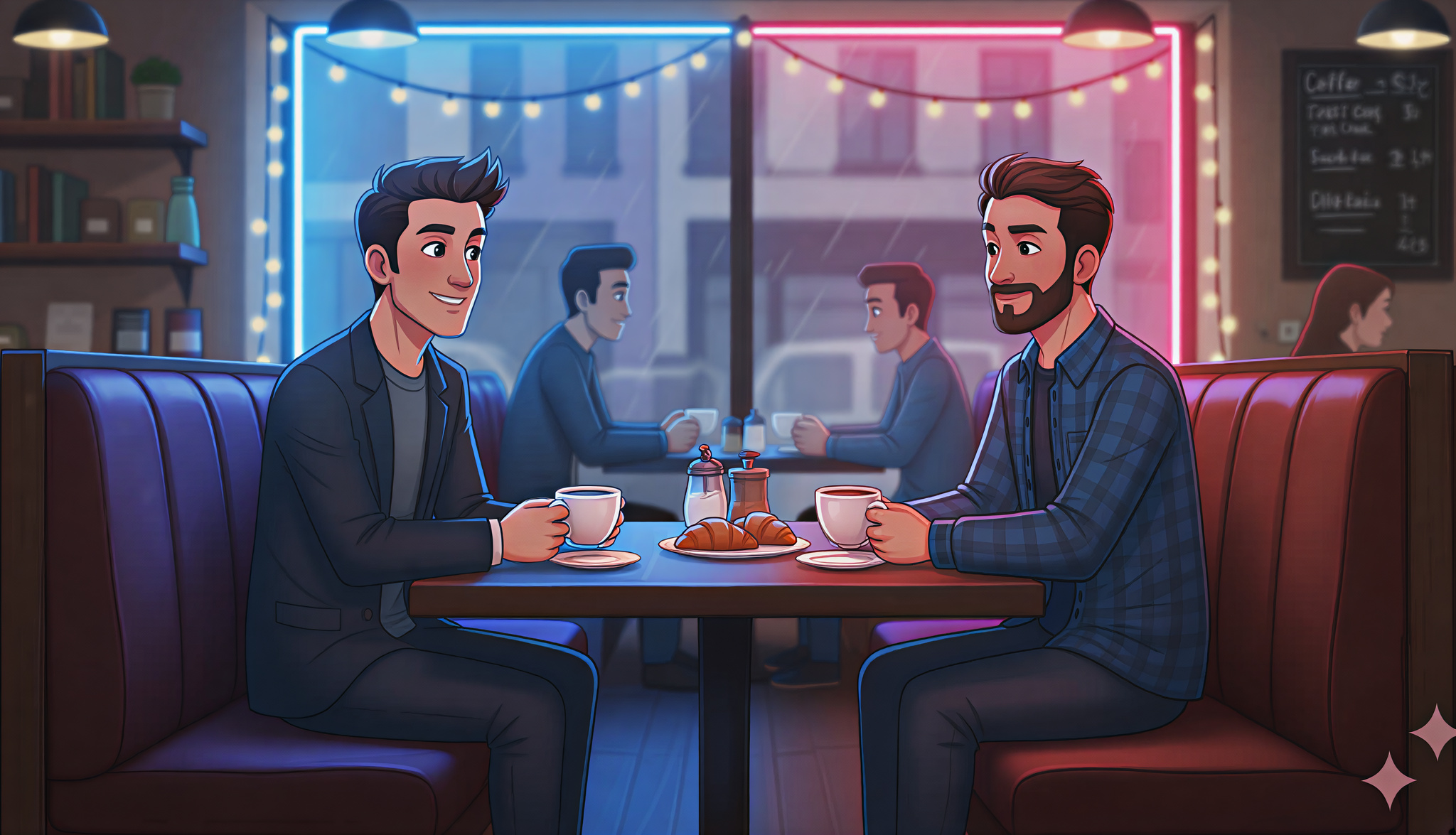
Lighting isn’t just technical — it’s emotional. The way a scene is lit can completely transform how we feel about it. In traditional cinematography, lighting guides the viewer’s attention, defines texture and tone, and communicates mood before a single word is spoken. The same principles apply when you’re generating imagery or video using AI.
If you’ve already read our guide on Cinematic Shot Types for AI art and how framing shapes storytelling, lighting is the next piece of the puzzle. Once you understand how to frame your shot, the right light makes it come alive.
Below are some of the foundational lighting styles and how you can use them when crafting AI-generated visuals. I took the same base image and applied the different lighting effects mentioned to show how they radically alter the scene.
High Key
Bright, even lighting with minimal shadows. It feels upbeat, friendly, and polished — the hallmark of commercials, sitcoms, and lifestyle content.
Use it for: Brand videos, corporate imagery, product showcases, or when you want a clean, optimistic tone.
Prompt cues: “High key lighting, minimal shadows, evenly lit studio, vibrant colors.”
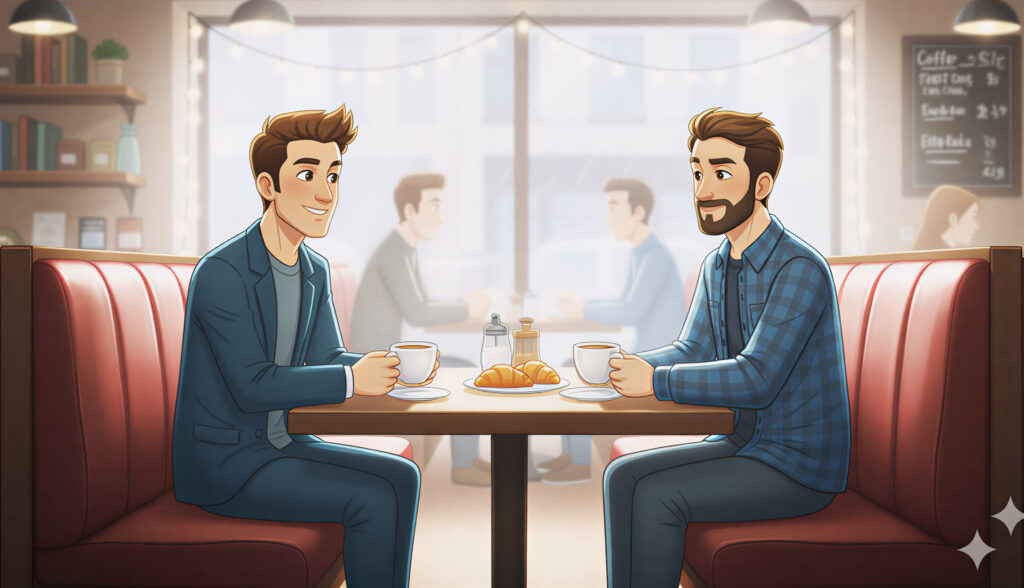

Low Key
Strong contrast between light and dark. Deep shadows, dramatic highlights, and a sense of mystery or tension.
Use it for: Cinematic storytelling, luxury brands, suspenseful scenes, emotional portraits.
Prompt cues: “Low key cinematic lighting, high contrast, moody shadows, film noir style.”
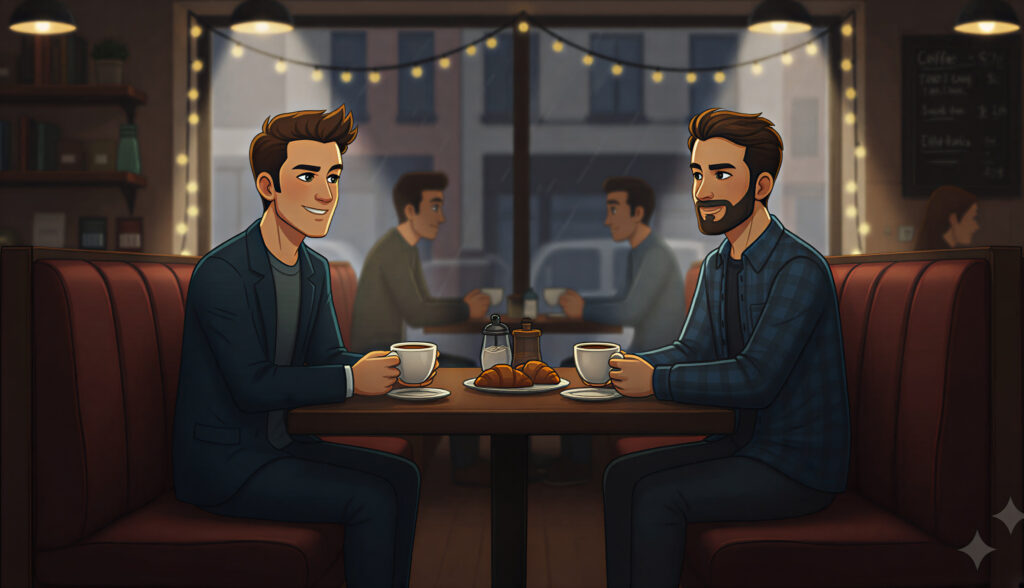

Soft Light
Diffused and natural. It wraps around the subject gently, creating flattering skin tones and a calm, intimate feel.
Use it for: Human-focused scenes, lifestyle photography, emotional storytelling.
Prompt cues: “Soft natural light, diffused glow, golden hour tone, gentle shadows.”
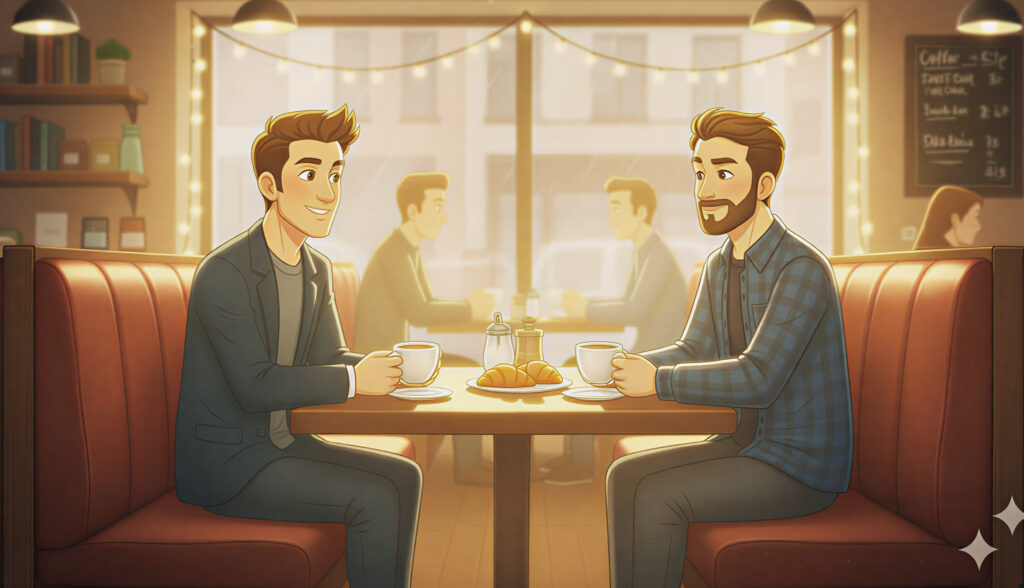

Hard Light
Defined shadows, strong directional light, and crisp contrast. It adds intensity and boldness to a scene.
Use it for: Fashion shoots, dramatic moments, energetic or stylized visuals.
Prompt cues: “Hard directional lighting, sharp shadows, sunlight through blinds, dramatic tone.”
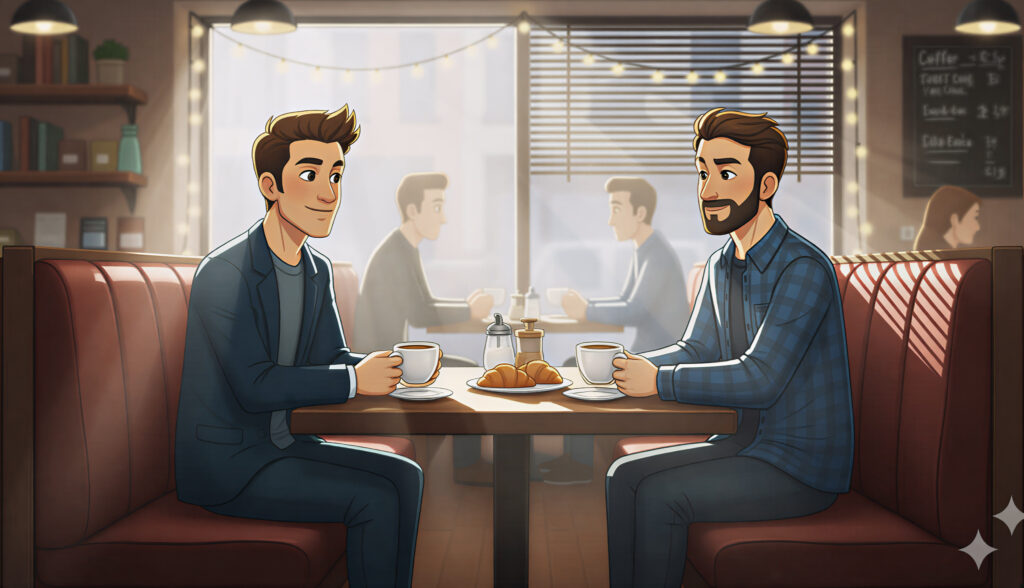

Backlight / Rim Light
Light from behind separates the subject from the background, creating a glowing outline or halo. It gives scenes depth and dimensionality.
Use it for: Hero shots, silhouettes, music videos, or when you want a sense of power or elevation.
Prompt cues: “Backlit subject, glowing edge light, cinematic rim lighting, lens flare.”
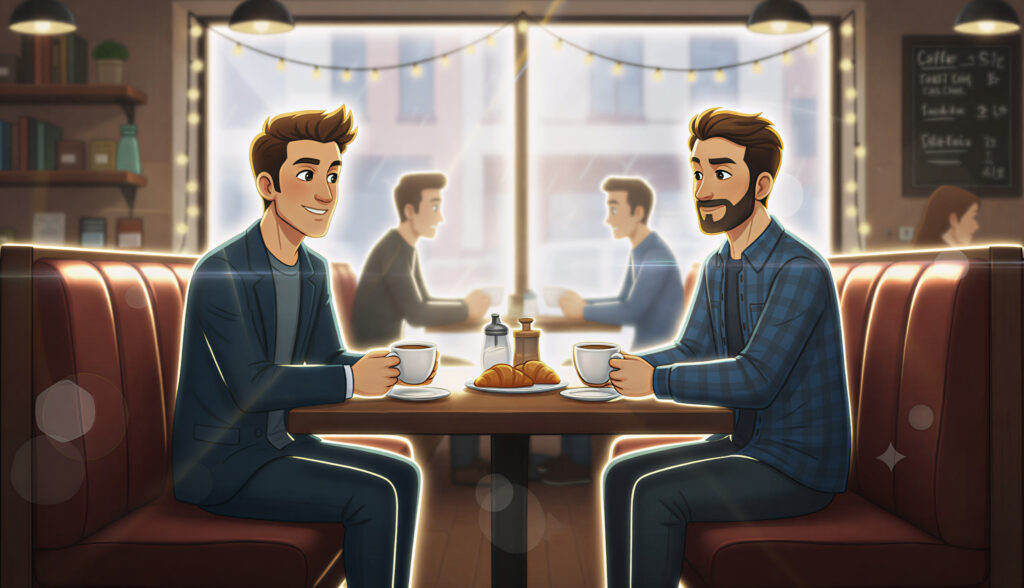

Practical Lighting
Using visible light sources within the scene itself — lamps, neon signs, headlights. It adds realism and atmosphere.
Use it for: Story-driven visuals, urban scenes, cozy interiors, or emotional realism.
Prompt cues: “Practical lighting from lamp or neon, cinematic ambience, warm glow, film grain.”
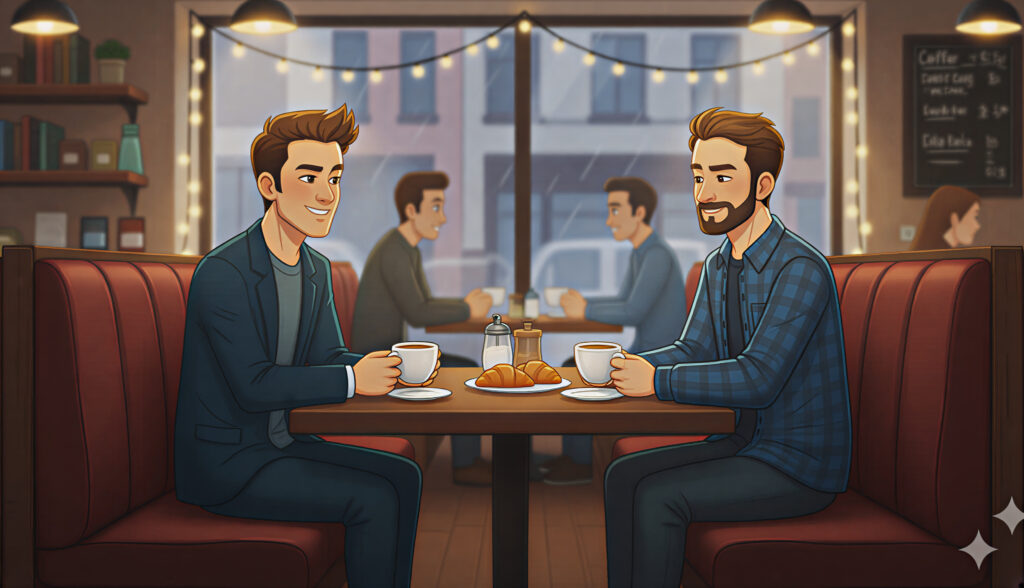

Color and Emotion
Lighting color changes everything. Blue tones evoke calm or sadness, orange feels warm and nostalgic, red feels dangerous or passionate. AI tools are great at exaggerating these moods when you’re intentional about your color palette.
Prompt cues: “Moody teal and orange lighting,” “soft pink lighting for romantic tone,” “neon blue and red contrast lighting.”
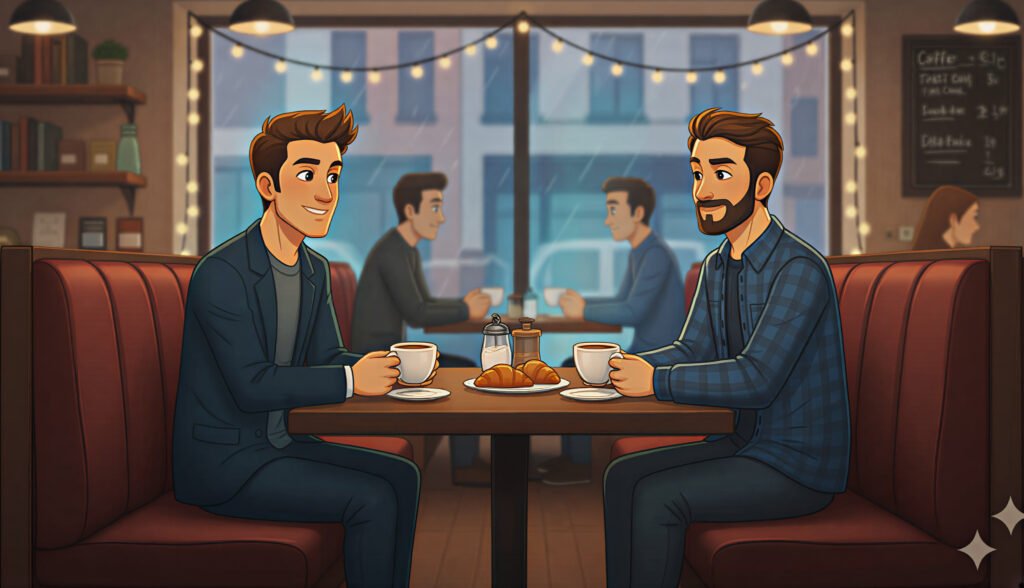
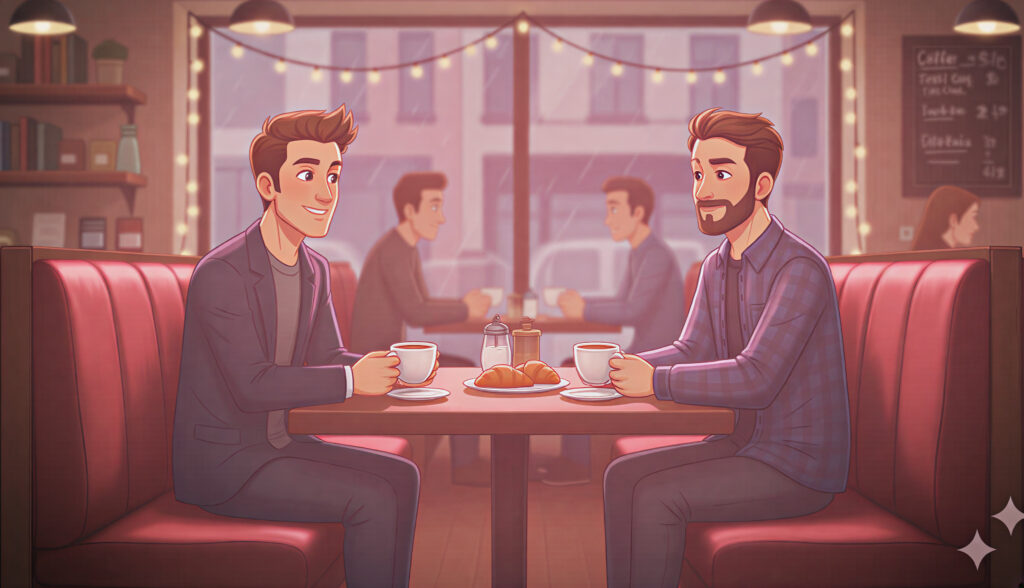
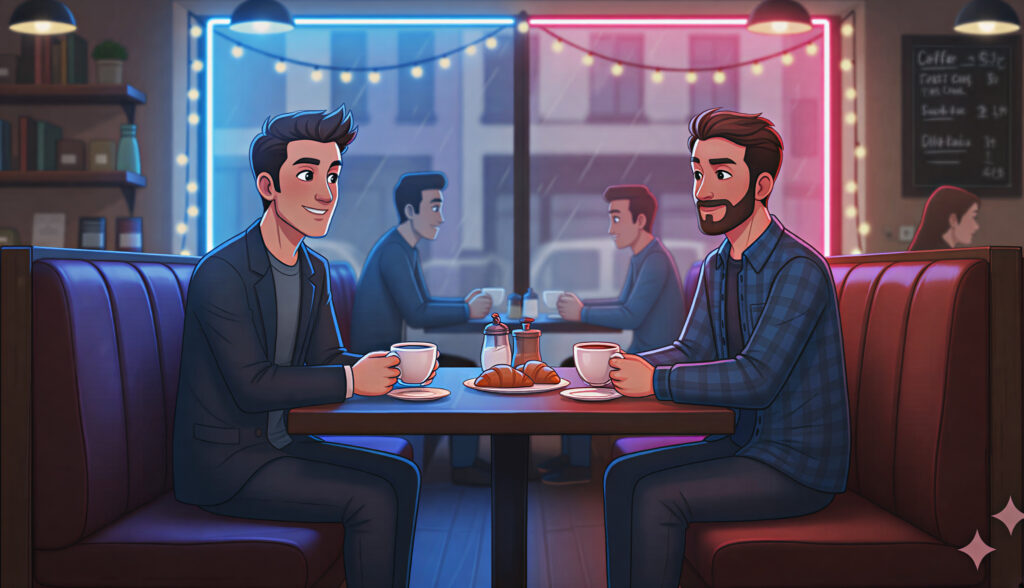



Final Thoughts
Cinematic lighting is the bridge between realism and storytelling. Whether you’re shooting a film or building visuals in AI, light guides emotion. Learn to control it, and your audience will feel exactly what you want them to feel.